It is important to create the correct environment for TPM; Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is about creating a culture within your organization where operators have ownership of their equipment and control the performance.
Wikipedia describes one of the main objectives of Total Productive Maintenance is to increase the productivity of plant and equipment with a modest investment in maintenance.
One thing is for certain, implementing Total Productive Maintenance is a big challenge, meet that challenge and deliver superior results.
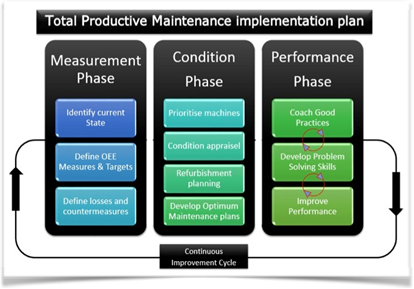
Following a 3 Phase Implementation plan does it every time.
5 Principles of TPM1
- Maximizing equipment effectiveness to improve productivity.
- Establish PM system focusing on the entire equipment life.
- Coordinate all departments, including those that design, maintain and operate equipment.
- Involving everyone, from top executives to shop floor employees.
- Managing through team-based activities aimed at plant wide goals of zero losses.
1 The Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance, TPM for every Operator, Productivity Press Portland Oregon, USA, 1996
5 Pillars of TPM
TPM recognizes that the people most likely to first notice equipment abnormalities are those who spend their working time at these machines. Therefore, involving these employees provides significant opportunities for early detection – and prevention – of breakdowns. This TPM approach provides another example of how Lean systems recognize the importance of all employees and provide mechanisms for actively engaging employees in improvement activities. Eliminating breakdowns is one of the main characteristics of TPM, and this is heavily dependent on preventive actions. There are five pillars of TPM2 , which must be pursued if a zero – or near zero – breakdown condition is to be achieved.
These are:
1 Improvement activities to increase equipment effectiveness
‣ Identify the 6 big losses OEE improvement
Request your free copy today, click the cover below
2 Autonomous maintenance
‣ Equipment operators Cleaning equipment
‣ Improving ease of cleaning & inspection
‣ Establishing cleaning & lubrication standards
3 Planned maintenance system
‣ Daily & periodic inspection & maintenance
‣ Predictive maintenance
‣ Breakdown analysis
‣ Lubrication & spare parts control
4 Operation and maintenance skills training
‣ Repair skills
‣ Troubleshooting & diagnostics
‣ Predictive technology
5 Maintenance prevention equipment design system
- Establish design goals
- Reduce life cycle costs
- Improve maintainability, reliability & operability
2 Productivity Press Development Team, TPM for Supervisors, Productivity Press, New York, 1992 Pp 30-38
Sustainability
Maximizing the likelihood that a culture of Total Productive Maintenance will be created at your organization involves more than the quality of delivery. Before during and after you begin adopting TPM you can create the environmental factors that will enable sustainability and support the growth.
Systems:
First stage in delivering reliability in your processes is to have the right system in place to enable the standardization of process steps and problem solving structures, Measuring OEE and identifying losses from the perspective of the classes 6 losses is a good place to start, learn where your opportunities are and prioritize resources to eliminate.
Business Processes:
Creating documents that visually communicate standardized working practices around your systems ensures repeatability, this promotes continuous improvement and reduces variability and clarifies who is playing to what position.
Training:
Training is about ensuring all stakeholders understand how to use any new systems or working practices so that new capabilities are developed and gaps can be closed.
Performance:
Performance Management is about reviewing, coaching and protecting improvements and ensuring that the cultural changes being sought are occurring at the correct pace.